Prostate Biopsy
A prostate gland biopsy is a test to remove small samples of prostate tissue to be examined under a microscope. For a prostate biopsy, a thin needle is inserted through the rectum (transrectal biopsy). The tissue samples taken during the biopsy are examined for cancer cells.
A biopsy may be done when a blood test shows a high level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) or after a rectal examination finds an abnormal prostate or a lump.
Why It Is Done?
A prostate biopsy is done to determine:
If a lump found in the prostate gland is cancer.
The cause of a high level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood.
How To Prepare?
Tell your Dr. Shusterman if you:
- Have had any bleeding problems.
- Are allergic to latex or any medicines, including anesthetics
- Take any medicines regularly. Be sure your doctor knows the names and doses of all your medicines.
- Are taking any blood-thinning medicines, such as warfarin (Coumadin), heparin, enoxaparin (Lovenox), aspirin, ibuprofen, or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Preparation:
- You will need to sign a consent form that says you understand the risks of a prostate biopsy and agree to have the biopsy done. Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have regarding the need for the biopsy, its risks, how it will be done, or what the results will mean.
- You need to take antibotics the day before the biopsy, the day of the biopsy and several days after the biopsy.
- You need to have an enema the night before and the morning of the biopsy.
- If the biopsy is done under anesthesia, Dr. Shusterman will tell you how soon before surgery to stop eating and drinking. Follow the instructions exactly about when to stop eating and drinking, or your surgery may be canceled. If the doctor has instructed you to take your medicines on the day of the surgery, please do so using only a sip of water.
- During preparation for the biopsy, an intravenous line (IV) maybe inserted in your arm, and a sedative medicine is given about an hour before the biopsy or a sedative can be given before the procedure orally to minimize discomfort.
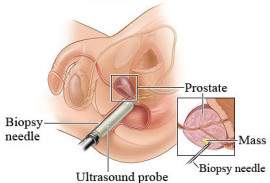
Through the rectum (transrectal biopsy)
We have the patient lie on his side. Dr. Shusterman will inject a local anesthetic around the prostate gland before the biopsy is taken.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is generally used to guide the needle to the correct biopsy location. A prostate biopsy is usually done with a spring-loaded needle. The needle quickly enters the prostate gland and removes a tissue sample. 12 samples are taken from different areas of the prostate. A transrectal biopsy takes about 4-5 minutes.
How It Feels
You may feel a slight sting when you receive an injection of medicine to numb your skin. You may feel a dull pressure as the biopsy needle is inserted. For a transrectal biopsy, you may feel pressure in the rectum while the ultrasound probe or guiding finger is in place. You also may feel a brief, sharp pain as the biopsy needle is inserted into the prostate gland. Usually several biopsy samples are collected.
Following the biopsy, you will be asked to avoid strenuous activities for about 4 hours. You may have mild pain in the pelvic area and blood in your urine for up to 5 days. Also, you may have some discoloration of your semen for up to one month after the biopsy. If you had a transrectal biopsy, you may experience a small amount of bleeding from your rectum for 2 to 3 days after the biopsy.
If you have a transurethral biopsy, you may have a urinary catheter in place for a few hours after the biopsy. You also may need to take an antibiotic medicine for several days after the biopsy.
If you have a general anesthetic, you will be in a recovery room for a few hours after the biopsy. You will need someone to drive you home when you are released. When you get home, your muscles may ache and you may feel tired for the rest of the day.
Risks
A prostate biopsy has a slight risk of causing problems such as:
- Infection. This is more common in men who have undiagnosed prostatitis. Usually, taking antibiotic medicine before the biopsy prevents an infection from developing.
- Bleeding into the urethra or bladder. This can cause a blood blister (hematoma), an inability to urinate, or a need to urinate often.
- Bleeding from the rectum. If you have a transrectal biopsy, you may experience a small amount of bleeding from your rectum for 2 to 3 days after the biopsy.
- An allergic reaction to the anesthetic medicines used during the biopsy.
After the biopsy
Call your doctor immediately if you:
- Have heavy bleeding or bleeding continues longer than 2 to 3 days.
- Have increased pain.
- Have a fever.
- Are unable to urinate within 8 hours or have blood in the urine for longer than 2 to 3 days.
Results
A prostate gland biopsy is a test to remove small samples of prostate tissue to be examined under a microscope. Results are usually available within 10 days.
|
Prostate biopsy |
|
|
Normal: |
The prostate gland tissue samples appear normal under the microscope, with no signs of infection or cancer. |
|
Abnormal: |
Cancer cells or signs of infection are found. |
|
Signs of an abnormal noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH),tuberculosis, lymphoma, or rectal or bladder cancer are present. |
|
If cancer cells are present, a grade (Gleason score) will be given, which your doctor will discuss with you. The Gleason score is considered a tool for predicting how aggressive the cancer is.
What Affects the Test?
Reasons you may not be able to have the test or why the results may not be helpful include:
- The biopsy may not contain enough tissue to make a diagnosis.
- A chance that a cancer may be missed since the biopsy takes a small amount of tissue.